Humidity
Absolute humidity
From the ideal gas law, the density of water,  w is given by
w is given by
 w= ( <mw>w fw e)/(R* T)
w= ( <mw>w fw e)/(R* T)
where <mw>w is the molecular weight of water (18.016 gm/mole), fw is a correction factor for non-ideal behavior which can be taken as fw = 1, e is the partial pressure of water, R* is the universal gas constant, and T is the local temperature.
Specific humidity
The total density,  , is given by the sum of dry and moist
densities ( i.e., assumes all other species are included in ``dry'').
, is given by the sum of dry and moist
densities ( i.e., assumes all other species are included in ``dry'').
 =
=  d +
d +  w = [ <mw>d · (P - fw e)]/(R* T)
+ (<mw>w fw e)/(R* T) =
[<mw>d · (P - 0.37803 fw e)]/(R* T)
w = [ <mw>d · (P - fw e)]/(R* T)
+ (<mw>w fw e)/(R* T) =
[<mw>d · (P - 0.37803 fw e)]/(R* T)
where <mw>d is the molecular weight of dry air (28.966), <mw>w/<mw>d = 0.62197, and (<mw>d - <mw>w)/<mw>d = 0.37803. The specific humidity is the ratio of the moist to total density and is dimensionless, but is usually expressed in gm/Kg units.
 w/
w/ = (0.62197 fw e) / (P - 0.37803 fw e)
= (0.62197 fw e) / (P - 0.37803 fw e)
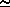 0.622 e/P
0.622 e/P
Note that
 w = q ·
w = q · 
and the volumetric mixing ratio, f, (i.e., ratio of water number density, Nw, to the total number density Nt) is given by
 Nw/Nt = <mw>/<mw>w · q
Nw/Nt = <mw>/<mw>w · q
where the average molecular weight, <mw>, is given by
Mass Mixing Ratio
 w/
w/ d = 0.62197 ·
[(fw e)/(P - fw e)]
d = 0.62197 ·
[(fw e)/(P - fw e)] 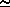 0.62197 ·
e/(P - e)
0.62197 ·
e/(P - e) 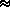 q
q
| Alt (km) | P (mB) | record low | 1% low | midlat. mean | 1% high | record high |
| sfc | 1013.25 | 0.1 | 5.0 | 4,686 | 30,000 | 35,000 |
| 1 | 890 | 24.0 | 27.0 | 3,700 | 29,000 | 31,000 |
| 2 | 790 | 21.0 | 31.0 | 2,843 | 24,000 | 28,000 |
| 4 | 610 | 16.0 | 24.0 | 1,268 | 18,000 | 22,000 |
| 6 | 470 | 6.2 | 12.0 | 554 | 7,700 | 8,900 |
| 8 | 350 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 216 | 4,300 | 4,700 |
| 10 | 265 | 5.3 | 43.2 | 1,300 | ||
| 12 | 195 | 1.2 | 11.3 | 230 | ||
| 14 | 140 | 1.5 | 3.3 | 48 | ||
| 16 | 100 | 1.0 | 3.3 | 38 |
% Relative Humidity
 100 · r/rs
100 · r/rs 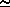 100 q/qs
100 q/qs
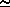 100 e/es
100 e/es
where rs  r(e = es) and qs
r(e = es) and qs  q(e = es).
q(e = es).
The saturated vapor pressure is approximately given by
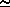 6.11 · 10[(a T)/(b + T)] mBar
6.11 · 10[(a T)/(b + T)] mBar
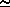 0.62197 · es/(P - es) for es > P
0.62197 · es/(P - es) for es > P
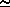 0.62197 for es
0.62197 for es 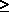 P
P
where T is given in °C and a and b are constants.
| a | b | |
| above water | 7.5 | 237.3 |
| above ice | 9.5 | 265.5 |
Dew Point Temperature
The Dew point is the temperature at which the partial pressure of water reaches the saturation value, that is
 w R* T)/(<mw>w fw) = es(Tdp)
w R* T)/(<mw>w fw) = es(Tdp)
The empirical expression for es can be used or a table lookup can be utilized after e is calculated.
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
