Cloud Clearing
Given the clear radiance, Rclr and the fraction of clouds,
 i in scene i.
i in scene i.
 i) · Rclr +
i) · Rclr +  i · Rcld
i · Rcld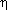 · ( R1 - R2 )
· ( R1 - R2 ) 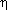

 1/(
1/( 2 -
2 -  1)
1)Chahine, M.T. 1974, J. Atmos. Sci. 31 p.233
Susskind, J., J. Joiner and C.D. Barnet 1995. Determination of
atmospheric and surface parameters from simulated AIRS/AMSU sounding
data. I. Retrieval methodology. submitted to J. Atmos. Oceanic
Tech. (JAOT) Sep. 1995.
N* method

 1/
1/ 2 =
(R1 - Rclr)/(R2 - Rclr)
2 =
(R1 - Rclr)/(R2 - Rclr)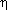 = N* / (1 - N*)
= N* / (1 - N*)McMillin, L.M. and C. Dean 1982. Evaluation of a new operational technique for producing clear radiances. J. Appl. Meteor. 21 p.1005-1014.
Smith, W.L. 1968. An improved method for calculating tropospheric
temperature and moisture from satellite radiometer measurements.
Monthly Weather Review 96 p.387-396.
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
