Potential Temperature
Derived directly from integration of the 1st law
of thermodynamics. It is the temperature
a parcel of air at P and T would have if it were at Ps. It is
conserved for adiabatic motions, ( i.e., d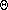 /dt = 0).
/dt = 0).
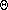 = T · (Ps/P)
= T · (Ps/P) =
P/(
=
P/( Rg) [(Ps/P)
Rg) [(Ps/P) ]
]
 = Rg/Cp
= Rg/Cp
For earth  = 0.286 (<mw> = 28.96, Cp =
1.004 Joules/gram/K). Some authors write this equation with
= 0.286 (<mw> = 28.96, Cp =
1.004 Joules/gram/K). Some authors write this equation with
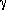 = Cp/Cv = 1/(1-
= Cp/Cv = 1/(1- )
)
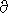 P/
P/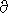 z = -
z = -  · g =
(P · g)/(Rg · T) = - P/H(z)
· g =
(P · g)/(Rg · T) = - P/H(z)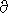 log(P) = -H(z) ·
log(P) = -H(z) · 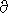 z
ztherefore,
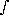 dz'/H(z')
dz'/H(z')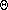 = T · e-
= T · e- 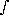 dz'/H(z')
dz'/H(z')if H(z) = H0
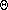 = T · e-
= T · e- · z/H0
· z/H0 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
