 r = (
r = ( Cp)/(4
Cp)/(4  T3
T3 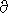
 /
/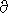 z)
z)
Harshvardan and Cess (1976, Tellus 28 p.1-10) give
a value for Earth CO2 of 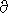
 /
/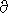 z = -0.0081
per Km and Cess and Khetan (1973, JQSRT 13 p.995-1009) give
a value for Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus of
z = -0.0081
per Km and Cess and Khetan (1973, JQSRT 13 p.995-1009) give
a value for Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus of
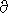
 /
/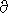 z = -0.0068, -0.0063, -0.0061, and
-0.0058 per Km, respectively.
z = -0.0068, -0.0063, -0.0061, and
-0.0058 per Km, respectively.
 r = (
r = ( H Cp)/(4
H Cp)/(4 
 T3)
T3)
The phase shift, 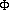 , is the seasonal lag due to the
radiative time constant. It arises from the 1st Fourier moment
of the thermal response. A value of
, is the seasonal lag due to the
radiative time constant. It arises from the 1st Fourier moment
of the thermal response. A value of  =90° indicates a full
seasonal shift ( e.g., the warm maximum expected at the summer
solstice would occur at the autumnal equinox).
=90° indicates a full
seasonal shift ( e.g., the warm maximum expected at the summer
solstice would occur at the autumnal equinox).
 = tan-1[ 2
= tan-1[ 2  ·
·  r/
r/ o ]
o ]
where  o is the orbital period. For
o is the orbital period. For  = 0.3
the values are:
= 0.3
the values are:
| Teff
K | Peff
mBar | 
gm/cm3 | H
Km |  rad rad
years | phase
° |
| Venus | 229.0 | 20.000 | 4.6230e-05 | 4.862 | 0.007 | 3.94 |
| Earth | 255.0 | 500.000 | 6.8297e-04 | 7.471 | 0.131 | 39.47 |
| Mars | 210.0 | 6.000 | 1.5124e-05 | 10.605 | 0.006 | 1.17 |
| Jupiter | 124.0 | 400.000 | 8.6132e-05 | 19.146 | 4.534 | 67.39 |
| Saturn | 95.0 | 300.000 | 8.1128e-05 | 36.975 | 20.794 | 77.27 |
| Uranus | 59.0 | 430.000 | 2.0161e-04 | 24.234 | 131.311 | 84.15 |
| Neptune | 59.0 | 500.000 | 2.3443e-04 | 19.206 | 121.008 | 77.67 |
| Titan | 85.0 | 1.000 | 4.0568e-06 | 18.152 | 0.053 | 82.54 |

 rad
rad PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
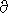 Q/
Q/ 1/
1/ · T4 ·
· T4 ·  /
/ , is the seasonal lag due to the
radiative time constant. It arises from the 1st Fourier moment
of the thermal response. A value of
, is the seasonal lag due to the
radiative time constant. It arises from the 1st Fourier moment
of the thermal response. A value of  ·
· 
