Dobson Units
 10-3 cm-amagat
10-3 cm-amagatgiven the number density, N, in molecules per cm3 then
 x = (<mw>x · Nx(z))/Na grams/cm2
x = (<mw>x · Nx(z))/Na grams/cm2
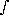 N(z) dz
N(z) dz 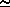 <N(L)> ·
<N(L)> · 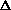 z =
<N(i)> ·
z =
<N(i)> · 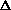 P/(
P/( t g) =
q · Na ·
t g) =
q · Na · 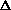 P/(<mw> g) molecules/cm2
P/(<mw> g) molecules/cm2Note that
 = q ·
= q ·  t = N · <mw> /Na where q is the
volumetric mixing ratio of the species being measured.
t = N · <mw> /Na where q is the
volumetric mixing ratio of the species being measured.To convert to mass column density, M, in grams per cm2
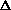 P/ g
P/ g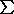 C(L) / N0
C(L) / N0where N0 is Loschmidt's number.
The atmosphere consists of fixed gases (e.g., CO2,
N2O, CO), water, and ozone so the pressure within any level
is given as
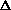 p(L)
p(L) 
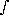
 t g dz =
g
t g dz =
g 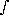 (
( f +
f +  w +
w +  o) dz
o) dzso that
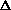 p(L) · Na / g =
<mw>f · Cf(L) + <mw>w · Cw(L) + <mw>o · Co(L)
p(L) · Na / g =
<mw>f · Cf(L) + <mw>w · Cw(L) + <mw>o · Co(L)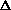 p(L) · Na)/(<mw>f · g)
- (<mw>w/<mw>f) · Cw(L)
- (<mw>o/<mw>f) · Co(L)
p(L) · Na)/(<mw>f · g)
- (<mw>w/<mw>f) · Cw(L)
- (<mw>o/<mw>f) · Co(L) we can also define the total column density as
 (
(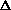 p(L) · Na) /
(<mw>(L) · g)
p(L) · Na) /
(<mw>(L) · g)and if we require
then,
Ct(L) in eqn 6 and <mw> can be solved for iteratively with an initial guess of <mw> = <mw>f
The volumetric mixing ratio, i.e., molecules of species x to the total number of molecules, is given by
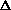 P(L) · Na) · <mw>(L) · g
P(L) · Na) · <mw>(L) · g PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
