Saturation Vapor Pressure
Given T in Kelvin these equations will give es in milliBar.
from Fleagle and Businger, Vol.5, pg. 62 (QC880.F59)
The first law can be written as
 2 -
2 -  1)
1)
where  1
1  1/
1/ 1 and index 1 refers to the liquid
phase and index 2 refers to the gas phase.
1 and index 1 refers to the liquid
phase and index 2 refers to the gas phase.
For an isothermal change of phase, the Clausius-Clapeyron equation has the form
d Ps/d T = L/[T · ( 2-
2- 1)]
1)]
Water vapor behaves like an ideal gas and  2
2 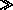
 1
for a change in state.
1
for a change in state.
L 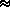 2.5 · 103 Joules/gm
2.5 · 103 Joules/gm
L 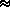 2.824 · 103 Joules/gm over ice
2.824 · 103 Joules/gm over ice
Rw = R*/<mw>w = 8.3143/18.016 = 0.4615 Joules/gm/K
Ps =  2 · Rw T
2 · Rw T
d Ps/d T = L/[T · ( 2-
2- 1)]
1)] 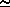 (L ·
(L ·  2)/T = (L · Ps) /(Rw · T2)
2)/T = (L · Ps) /(Rw · T2)
d log(es) = d Ps/Ps = (L/Rw) · (dT/T2)
loge(es) = 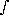 (L/Rw) · (dT/T2) =
-(L/Rw)|T->T0 + C =
-L/(Rw · T0) + L/(Rw· T) + C
(L/Rw) · (dT/T2) =
-(L/Rw)|T->T0 + C =
-L/(Rw · T0) + L/(Rw· T) + C
at triple point all 3 phases can exist in equilibrium, 0.0098° C and Ps = 6.11 mB
es(T=T0) = 6.11
L/Rw = 5417.12
L/(Rw T0) = 19.8313
6.11 · exp[ L/(Rw T0) ] = 2.504 · 109
es(T) = 6.11 · exp[ 5417( 1/T0 - 1/T) ] = 2.504 · 109 · exp[ 5417/T ]
Undocumented fit is used in the program watsat.F (over liquid)
es = 2.229 · 109 · exp[ -5385/T ]
Note this is the same equation as above, except that it assumes L = 2485.2 Joules/gm and T0 = 273.15 ° K
Another undocumented fit is given (but not used) in the program watsat.F
es = 0.001 · exp[ a/T + b + c log(T) + d · T + e · T2 ]
| coef | over ice | over water |
| a | -5631.1206 | -2313.0338 |
| b | -8.363602 | -164.03307 |
| c | 8.2312 | 38.053682 |
| d | -3.861449 · 10-2 | -1.3844344 · 10-1 |
| e | 2.77494 · 10-5 | 7.4465367 · 10-5 |
From Rogers and Yau, pg. 16
es = 6.112 · exp[ a · (T-273.16)/(T-b) ]
| coef | Rogers & Yau over water |
| a | 17.67 |
| b | 29.66 |
Murray, F.W. 1966. ``On the computation of Saturation Vapor Pressure'' J. Appl. Meteor. 6 p.204
es = 6.1078 · exp[ a · (T-273.16)/ (T-b) ]
| coef | Murray over ice | Murray over water |
| a | 21.8745584 | 17.2693882 |
| b | 7.66 | 35.86 |
Saucier, W.J. 1883. ``Principles of Meteorological Analysis'' Dover pg. 9 who uses values of Tetens (1930). Note, he used 10[(a'T)/(T-b')] with T in Centigrade so to convert into the form above a = log 10 · a' and b = 273.16-b'.
| coef | over ice | over water |
| a | 21.875 | 17.27 |
| b | 7.66 | 35.86 |
 PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
PDS: The Planetary Atmospheres Node
